Secure Remote Login IoT Password: A Comprehensive Guide To Protecting Your Devices
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, securing remote logins for IoT devices has become a critical issue for both individuals and organizations. IoT devices are now an integral part of our daily lives, from smart homes to industrial automation. However, the rapid expansion of IoT devices has also opened the door to various security vulnerabilities, making it essential to understand how to protect your devices with strong passwords and secure login protocols.
With billions of connected devices worldwide, ensuring the security of remote logins is no longer optional. Weak passwords and insecure authentication methods can expose sensitive data, compromise personal privacy, and even cause financial losses. This comprehensive guide explores the best practices for securing remote logins in IoT devices and explains how to protect your devices from potential threats.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of secure remote logins, discuss common vulnerabilities, and provide actionable steps to enhance the security of your IoT devices. Whether you're a homeowner with smart devices or an IT professional managing a network of IoT systems, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to safeguard your digital assets.
Read also:Yoo Jungii A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Why Secure Remote Login for IoT Devices Matters
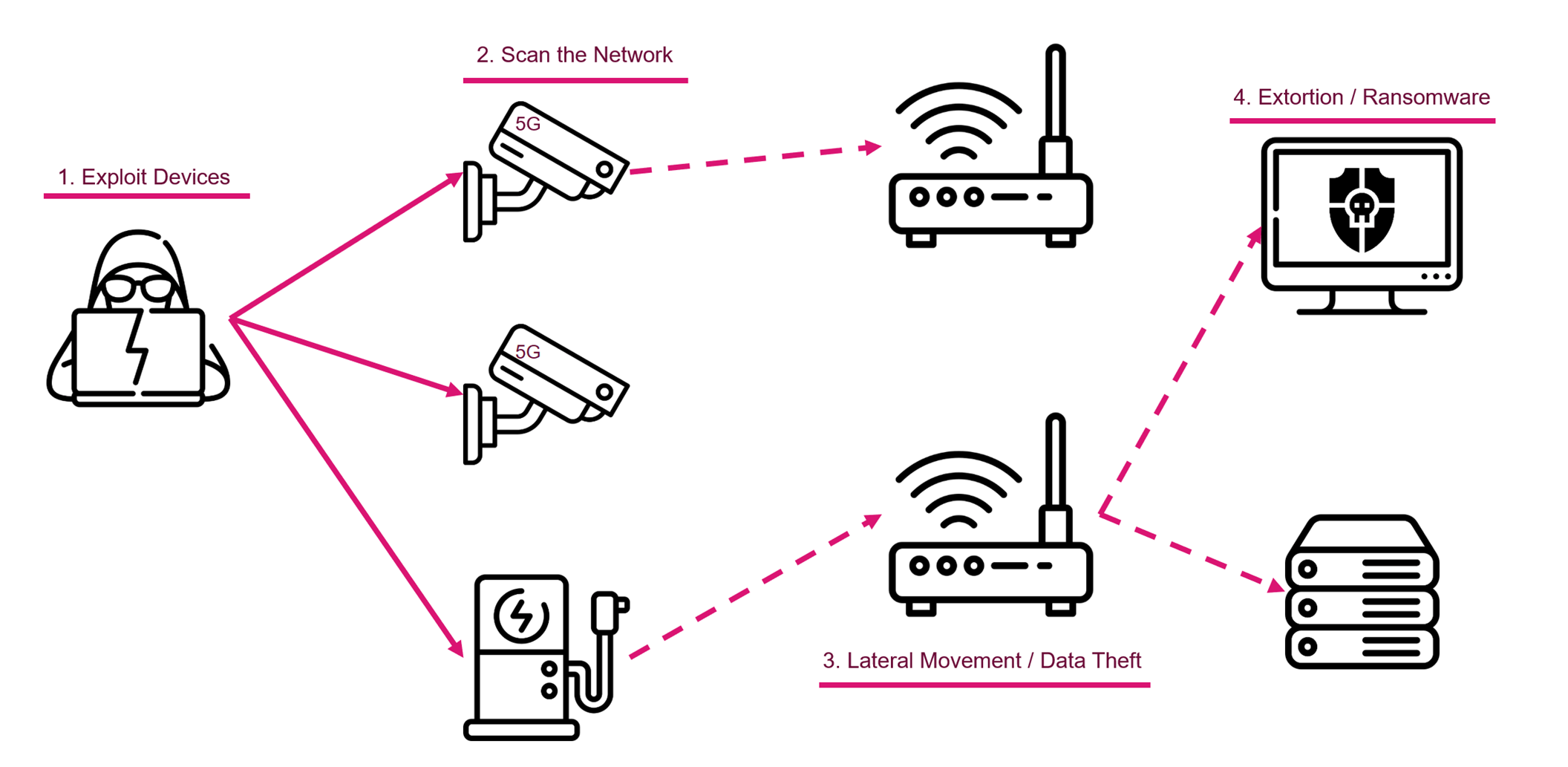
IoT devices are designed to make life easier by automating tasks and providing instant access to information. However, the convenience they offer comes with significant security risks. A secure remote login is crucial because it acts as the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Without proper security measures, hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in IoT devices to gain access to sensitive data, control systems, or launch large-scale cyberattacks.
The Growing Threat Landscape
The number of IoT devices is projected to exceed 25 billion by 2030, according to a report by Statista. With this growth comes an increased risk of cyberattacks. Many IoT devices are shipped with default passwords that users often fail to change, making them easy targets for attackers. In 2020 alone, the number of IoT-related cyberattacks increased by 300%, highlighting the urgent need for better security practices.
Impact of Insecure Logins
An insecure remote login can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Data breaches that compromise personal or corporate information.
- Unauthorized access to critical systems, leading to operational disruptions.
- Financial losses due to stolen credentials or ransomware attacks.
- Damage to reputation, especially for businesses managing IoT networks.
Common Vulnerabilities in IoT Remote Logins
Understanding the vulnerabilities in IoT remote logins is the first step toward securing your devices. Below are some of the most common issues that make IoT devices susceptible to attacks:
Default Passwords
Many IoT devices come with default passwords that are publicly available. If users fail to change these passwords after installation, attackers can easily gain access to the devices. According to a study by Kaspersky, over 60% of IoT devices still use default credentials, making them prime targets for brute-force attacks.
Weak Passwords
Even when users change default passwords, they often choose weak ones that are easy to guess. Common mistakes include using predictable sequences (e.g., "123456"), personal information (e.g., birthdays), or overly simple phrases (e.g., "password"). Such passwords can be cracked within seconds using modern password-cracking tools.
Read also:Richard Dean Anderson The Iconic Star Of Tv And Film
Insecure Communication Protocols
Some IoT devices use outdated or insecure communication protocols, such as HTTP instead of HTTPS. This exposes data transmitted between the device and the server to interception and eavesdropping. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to steal login credentials or inject malicious code into the communication stream.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Remote Logins
Securing remote logins for IoT devices requires a combination of strong authentication methods, robust password management, and regular security updates. Below are some best practices to enhance the security of your IoT devices:
Create Strong and Unique Passwords
A strong password is the foundation of secure remote logins. Follow these guidelines when creating passwords for your IoT devices:
- Use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid using easily guessable information, such as names or birthdays.
- Ensure passwords are at least 12 characters long.
- Use a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification before accessing a device. This could include something you know (password) and something you have (a one-time code sent to your phone). Enabling 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
Regularly Update Firmware and Software
Manufacturers frequently release updates to address security vulnerabilities and improve device performance. Keeping your IoT devices up to date ensures that they are protected against the latest threats. Set up automatic updates whenever possible to avoid missing critical patches.
Advanced Security Measures for IoT Remote Logins
For organizations and individuals seeking an extra level of security, advanced measures can further enhance the protection of IoT devices:
Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control restricts access to devices based on user roles and responsibilities. This ensures that only authorized personnel can perform specific actions, reducing the risk of accidental or malicious misuse. RBAC is particularly useful in enterprise environments where multiple users interact with IoT devices.
Use Encryption for Data Transmission
Encrypting data transmitted between IoT devices and servers prevents attackers from intercepting sensitive information. Always use secure communication protocols, such as HTTPS or SSH, and ensure that encryption keys are stored securely. End-to-end encryption provides the highest level of protection by encrypting data at both the source and destination.
Monitor for Suspicious Activity
Implementing intrusion detection systems (IDS) and log analysis tools can help identify and respond to suspicious activity in real-time. These systems can alert administrators to potential threats, allowing them to take immediate action to mitigate risks. Regularly reviewing logs and security reports is essential for maintaining the integrity of IoT networks.
How to Protect Your IoT Devices from Brute-Force Attacks
Brute-force attacks involve systematically trying different password combinations until the correct one is found. To protect your IoT devices from such attacks, consider the following strategies:
Limit Login Attempts
Restricting the number of login attempts allowed within a specific time frame can prevent attackers from testing multiple passwords. After a certain number of failed attempts, the system should temporarily lock the account or require additional verification steps.
Use Captcha for Additional Verification
Captcha challenges can deter automated brute-force attacks by requiring users to prove they are human. This simple measure adds an extra layer of protection without significantly impacting user experience.
Monitor Login Patterns
Analyzing login patterns can help identify potential brute-force attacks. For example, if a large number of login attempts originate from the same IP address or occur within a short time frame, this could indicate malicious activity. Implementing IP blocking or rate limiting can effectively mitigate such threats.
The Role of Password Managers in IoT Security
Password managers are invaluable tools for managing complex passwords across multiple devices. They securely store and autofill login credentials, eliminating the need to remember or write down passwords. When selecting a password manager for IoT devices, consider the following factors:
Security Features
Ensure the password manager uses strong encryption algorithms and offers additional security features, such as biometric authentication or multi-factor authentication. These features enhance the overall security of stored passwords and protect against unauthorized access.
Compatibility
Choose a password manager that is compatible with all your IoT devices and operating systems. This ensures seamless integration and consistent security across your network. Popular password managers, such as LastPass and Dashlane, offer cross-platform support and are compatible with most IoT devices.
User Experience
A user-friendly interface and intuitive design can significantly improve the adoption of password managers. Look for features like automatic password generation, password strength indicators, and regular security audits to enhance the user experience.
Case Studies: Real-World IoT Security Incidents
Learning from real-world incidents can provide valuable insights into the importance of securing IoT remote logins. Below are two notable examples:
Mirai Botnet Attack
In 2016, the Mirai botnet exploited weak passwords in IoT devices to create a massive network of compromised systems. This botnet launched a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack on major websites, causing widespread disruptions. The incident highlighted the vulnerabilities of IoT devices with default passwords and the need for stronger security measures.
Ring Doorbell Hack
In 2020, several Ring doorbell users reported unauthorized access to their devices, leading to privacy breaches and even harassment. The attackers exploited weak passwords and insufficient security protocols to gain control of the devices. This incident underscored the importance of securing IoT devices with strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication.
Future Trends in IoT Security
As IoT technology continues to evolve, so do the methods used to secure remote logins. Emerging trends in IoT security include:
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint scanning or facial recognition, offers a more secure alternative to traditional passwords. This method eliminates the need for users to remember complex credentials while providing a high level of security.
AI-Powered Security Solutions
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used to detect and respond to security threats in real-time. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, enabling them to predict and prevent potential attacks before they occur.
Blockchain for Secure Communication
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and tamper-proof method for securing communications between IoT devices. By recording transactions in an immutable ledger, blockchain ensures the integrity and authenticity of data transmitted across IoT networks.
Conclusion
Securing remote logins for IoT devices is essential in today's interconnected world. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can significantly enhance the security of your IoT devices and protect them from potential threats. Remember to use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and keep your devices up to date with the latest firmware and software updates.
We encourage you to share this article with others and leave a comment below if you have any questions or additional tips for securing IoT remote logins. Together, we can create a safer and more secure IoT ecosystem for everyone.
Table of Contents
- Why Secure Remote Login for IoT Devices Matters
- Common Vulnerabilities in IoT Remote Logins
- Best Practices for Securing IoT Remote Logins
- Advanced Security Measures for IoT Remote Logins
- How to Protect Your IoT Devices from Brute-Force Attacks
- The Role of Password Managers in IoT Security
- Case Studies: Real-World IoT Security Incidents
- Future Trends in IoT Security
- Conclusion