Understanding Schizophrenia: Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment
Schizophrenia is a complex mental health disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It disrupts the normal functioning of the brain and can lead to severe challenges in daily life. This condition is often misunderstood, but understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for providing support and care for those affected.
Schizophrenia affects approximately 20 million people worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Despite its prevalence, misconceptions surrounding the disorder continue to persist. It is crucial to educate ourselves about schizophrenia to reduce stigma and promote effective management strategies.
Living with schizophrenia can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for schizophrenia, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of this complex condition.
Read also:Stray Kids A Comprehensive Dive Into Their Journey And Success
Table of Contents
- What is Schizophrenia?
- Symptoms of Schizophrenia
- Causes of Schizophrenia
- Diagnosing Schizophrenia
- Treatment Options for Schizophrenia
- Living with Schizophrenia
- Support for Caregivers
- Schizophrenia and Society
- Myths and Facts About Schizophrenia
- Conclusion
What is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that impacts a person's perception of reality. It is characterized by a combination of positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms. This condition often begins in early adulthood and can significantly impair daily functioning if left untreated.
People with schizophrenia may experience hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. These symptoms can make it difficult for them to distinguish between what is real and what is imagined. Understanding the nature of schizophrenia is critical for developing empathy and providing appropriate care.
Research suggests that schizophrenia affects men and women equally, but men tend to develop symptoms earlier in life. Early detection and intervention are key to managing the condition effectively.
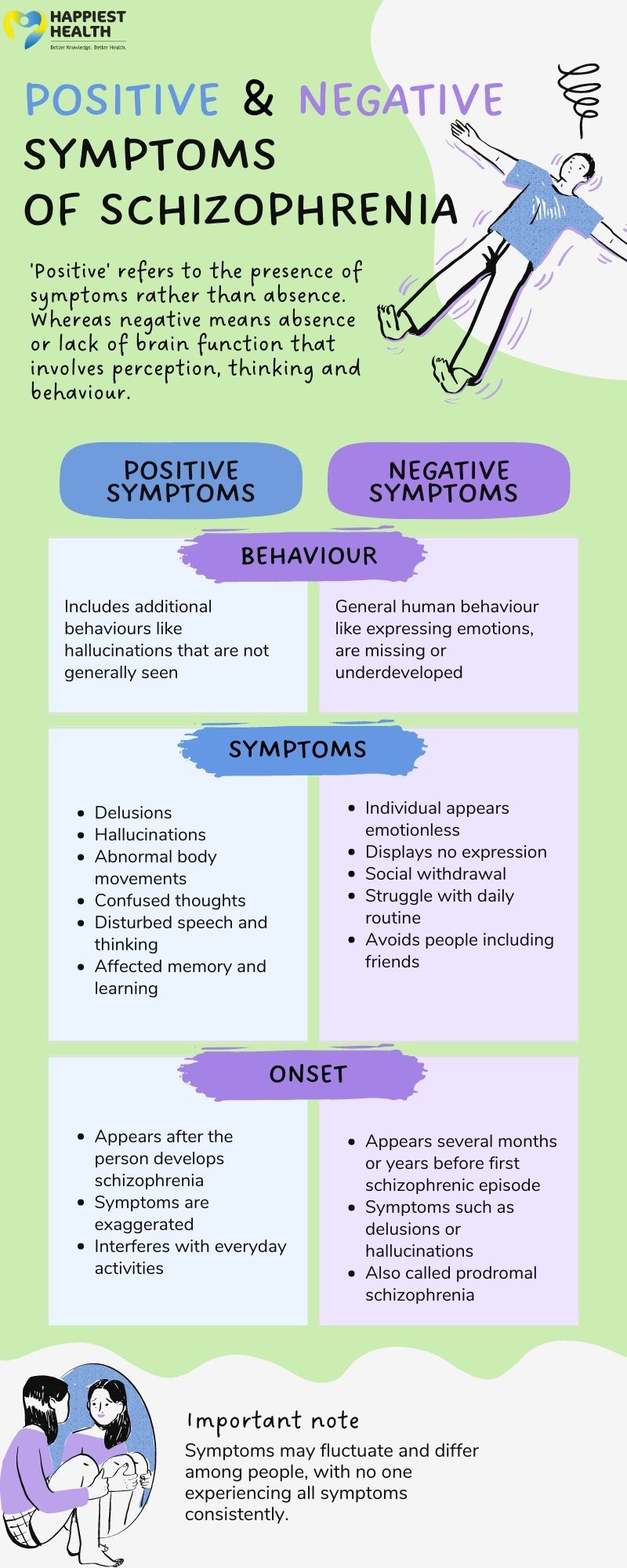
Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Positive Symptoms
Positive symptoms refer to the presence of abnormal behaviors not seen in healthy individuals. These include:
- Hallucinations: Hearing or seeing things that do not exist.
- Delusions: Holding false beliefs despite evidence to the contrary.
- Disorganized speech: Difficulty organizing thoughts and communicating effectively.
- Abnormal motor behavior: Unpredictable or erratic movements.
Negative Symptoms
Negative symptoms involve the absence or reduction of normal behaviors and emotions. Examples include:
- Flat affect: Reduced expression of emotions.
- Avolition: Lack of motivation or interest in activities.
- Asociality: Withdrawal from social interactions.
- Alogia: Decreased speaking or verbal output.
Cognitive Symptoms
Cognitive symptoms affect a person's ability to think clearly and make decisions. These may include:
Read also:Mike Adria The Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
- Impaired executive function: Difficulty planning and organizing tasks.
- Attention deficits: Trouble focusing on tasks or conversations.
- Memory problems: Challenges with remembering information or learning new things.
Causes of Schizophrenia
The exact cause of schizophrenia is not fully understood, but research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors contributes to its development. Some of the key factors include:
- Genetics: Schizophrenia tends to run in families, indicating a genetic component.
- Brain structure and chemistry: Abnormalities in brain structure and neurotransmitter levels, such as dopamine and glutamate, may play a role.
- Environmental factors: Stress, trauma, and substance abuse can increase the risk of developing schizophrenia.
A 2021 study published in the journal Nature Genetics identified over 100 genetic loci associated with schizophrenia, highlighting the complexity of its genetic basis.
Diagnosing Schizophrenia
Diagnosing schizophrenia involves a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional. The process typically includes:
- A thorough medical history review.
- A psychological assessment to evaluate symptoms and behaviors.
- Neurological and laboratory tests to rule out other conditions.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) provides specific criteria for diagnosing schizophrenia, including the presence of two or more characteristic symptoms for at least six months.
Treatment Options for Schizophrenia
Medication
Antipsychotic medications are the primary treatment for schizophrenia. These drugs help manage positive symptoms by regulating neurotransmitter levels in the brain. Commonly prescribed antipsychotics include:
- First-generation antipsychotics: Haloperidol, Fluphenazine.
- Second-generation antipsychotics: Risperidone, Olanzapine, Aripiprazole.
Psychosocial Interventions
In addition to medication, psychosocial interventions play a crucial role in schizophrenia treatment. These include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Helps individuals manage symptoms and improve functioning.
- Family therapy: Provides education and support for family members.
- Vocational rehabilitation: Assists individuals in finding and maintaining employment.
Living with Schizophrenia
Living with schizophrenia requires a comprehensive approach to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Strategies for living with schizophrenia include:
- Adhering to prescribed treatment plans.
- Building a strong support network of family, friends, and mental health professionals.
- Practicing self-care through healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Support for Caregivers
Caring for someone with schizophrenia can be emotionally and physically demanding. Caregivers should prioritize their own well-being by:
- Seeking support from local caregiver groups or online communities.
- Learning about the condition to better understand the challenges faced by their loved ones.
- Taking breaks and practicing self-care to prevent burnout.
Schizophrenia and Society
Society plays a significant role in shaping perceptions of schizophrenia. Stigma and discrimination against individuals with schizophrenia can exacerbate their symptoms and hinder recovery. Efforts to reduce stigma include:
- Public education campaigns to raise awareness about mental health issues.
- Advocacy for policies that promote mental health care access and equality.
- Encouraging open discussions about mental health to foster understanding and empathy.
Myths and Facts About Schizophrenia
Misconceptions about schizophrenia contribute to stigma and misunderstanding. Here are some common myths and facts:
- Myth: Schizophrenia means having a "split personality."
Fact: Schizophrenia is not the same as dissociative identity disorder. It involves disturbances in perception and thought processes. - Myth: People with schizophrenia are violent.
Fact: Most individuals with schizophrenia are not violent and are more likely to withdraw from social interactions. - Myth: Schizophrenia cannot be treated.
Fact: With proper treatment and support, many people with schizophrenia can lead productive and fulfilling lives.
Conclusion
Schizophrenia is a complex mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for providing effective care and support. By addressing stigma and promoting awareness, we can create a more inclusive and compassionate society for individuals living with schizophrenia.
We encourage readers to share this article and engage in discussions about mental health. If you or someone you know is struggling with schizophrenia, seek professional help and explore available resources. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by this condition.