Securing Remote SSH Access: A Comprehensive Guide For Enhanced Cybersecurity
Securing remote SSH access has become a critical aspect of modern cybersecurity practices. As more businesses and individuals rely on remote work setups, ensuring the security of SSH connections is paramount to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. SSH, or Secure Shell, is a network protocol that provides secure communication between two systems over an unsecured network. However, as the use of SSH grows, so does the risk of cyberattacks targeting SSH connections. This article will explore the best practices, tools, and strategies to secure your remote SSH access effectively.
With the rise of remote work, organizations must prioritize securing SSH access to safeguard their infrastructure and data. Weak SSH configurations can lead to significant vulnerabilities, exposing critical systems to malicious actors. This guide will provide a detailed overview of SSH security, including step-by-step instructions and expert-recommended strategies to enhance your remote SSH access security.
Whether you're an IT professional, system administrator, or a small business owner, understanding how to secure remote SSH access is essential. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your digital assets from potential threats. Let's dive into the world of SSH security and discover how you can fortify your remote connections.
Read also:Emily Ellen Rudd Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Introduction to SSH
- Why Secure SSH Connections?
- Common SSH Security Threats
- Best Practices for SSH Security
- SSH Configuration Tips
- Using SSH Keys for Authentication
- Monitoring SSH Activity
- Tools for SSH Security
- Common SSH Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion
Introduction to SSH
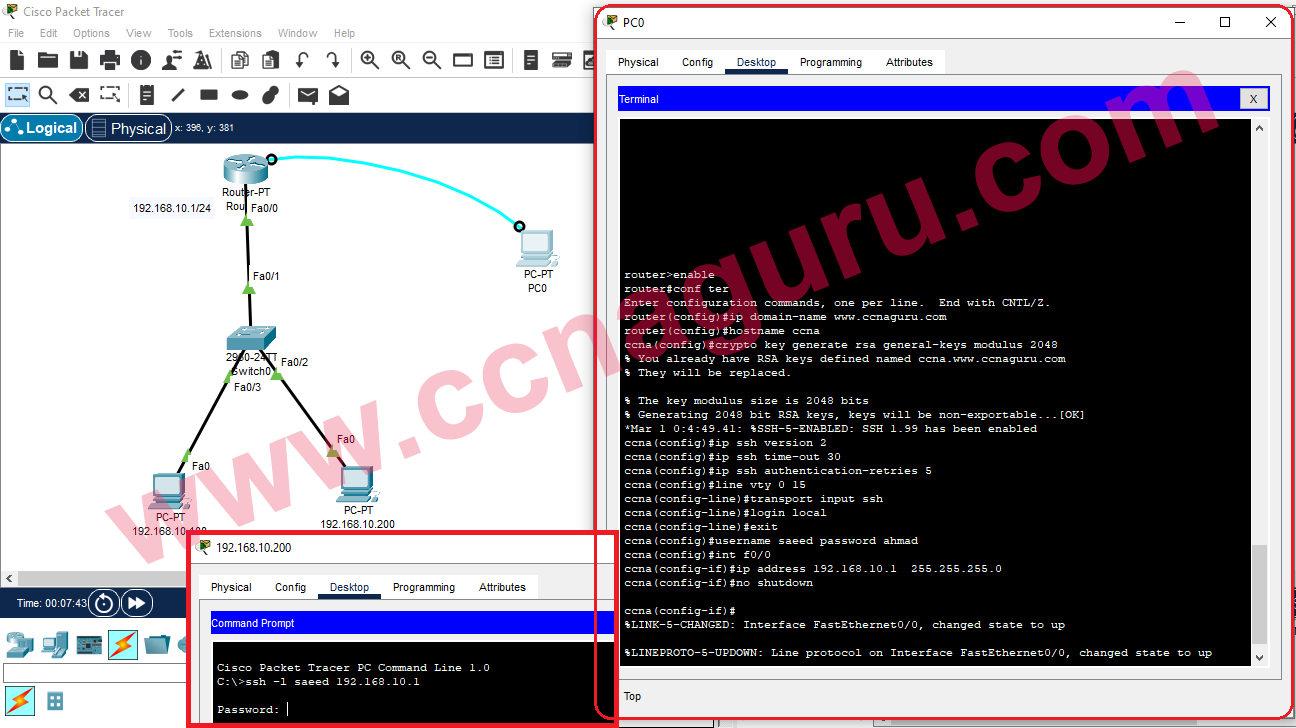
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol designed to provide secure communication between two systems over an unsecured network. Initially developed in 1995 as a replacement for less secure protocols like Telnet, SSH has become a cornerstone of modern network security. It allows users to execute commands remotely, transfer files securely, and manage networked devices with encryption.
SSH operates on a client-server model, where the client initiates the connection and the server authenticates the client before granting access. The protocol ensures confidentiality, integrity, and authentication of data transmitted between the client and server. As remote work and cloud computing continue to grow, securing remote SSH access has become more important than ever.
How SSH Works
SSH establishes a secure connection through a combination of encryption, authentication, and data integrity mechanisms. Here's a brief overview of the SSH process:
- Key Exchange: The client and server exchange cryptographic keys to establish a secure session.
- Authentication: The client proves its identity to the server using either password-based or key-based authentication.
- Encryption: All data transmitted between the client and server is encrypted to prevent eavesdropping.
- Data Integrity: SSH ensures that data has not been tampered with during transmission.
Why Secure SSH Connections?
Securing remote SSH access is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of your systems. Without proper security measures, SSH connections can become vulnerable to various cyber threats. Below are some compelling reasons to prioritize SSH security:
Protect Sensitive Data
SSH connections often involve the transfer of sensitive information, such as user credentials, configuration files, and proprietary data. By securing SSH access, you can prevent unauthorized access and ensure that your data remains confidential.
Prevent Unauthorized Access
Weak SSH configurations can allow malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to your systems. This can lead to data breaches, system compromise, and financial losses. Implementing robust security measures can significantly reduce the risk of such incidents.
Read also:The Remarkable Life Story Of Catherine Bolle The Mother Of Josh Brolin
Compliance and Legal Requirements
Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate the protection of sensitive data. Securing SSH access helps organizations comply with these regulations and avoid potential legal consequences.
Common SSH Security Threats
Despite its robust security features, SSH is not immune to cyber threats. Below are some common SSH security threats that organizations should be aware of:
Brute Force Attacks
Brute force attacks involve automated tools attempting to guess SSH passwords by trying numerous combinations. Weak or predictable passwords make systems more vulnerable to such attacks.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
In a MitM attack, a malicious actor intercepts and alters communications between the client and server. This can lead to data theft or unauthorized access if proper encryption and authentication mechanisms are not in place.
Configuration Errors
Improper SSH configurations, such as allowing password-based authentication or using default ports, can create vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit.
Best Practices for SSH Security
Implementing best practices for SSH security is essential to protect your systems and data. Below are some expert-recommended strategies to enhance your remote SSH access security:
Use Strong Passwords
Strong passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to create complex passwords.
Disable Password-Based Authentication
Password-based authentication can be easily compromised through brute force attacks. Disabling this method and switching to key-based authentication can significantly enhance SSH security.
Limit User Access
Restrict SSH access to only those users who require it. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that users have the minimum privileges necessary to perform their tasks.
SSH Configuration Tips
Proper SSH configuration is crucial for ensuring the security of your remote connections. Below are some tips to help you configure SSH securely:
Change the Default SSH Port
Using the default SSH port (22) makes your system an easy target for automated attacks. Changing the port to a non-standard number can help reduce the risk of such attacks.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification before gaining access. This can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Regularly Update SSH Software
Keeping your SSH software up to date ensures that you have the latest security patches and features. Regular updates can help protect your system from known vulnerabilities.
Using SSH Keys for Authentication
SSH keys provide a more secure alternative to password-based authentication. They consist of a public key, which is stored on the server, and a private key, which is kept securely on the client's machine. Below are some benefits of using SSH keys:
Increased Security
SSH keys are much harder to crack than passwords, making them a more secure authentication method.
Convenience
Once set up, SSH keys allow users to log in without entering a password, streamlining the authentication process.
Flexibility
SSH keys can be easily revoked or replaced if compromised, providing greater flexibility in managing access.
Monitoring SSH Activity
Monitoring SSH activity is essential for detecting and responding to potential security threats. Below are some strategies for effective SSH monitoring:
Log Analysis
Regularly reviewing SSH logs can help identify suspicious activity, such as multiple failed login attempts or unauthorized access attempts.
Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
IDS tools can automatically detect and alert you to potential SSH attacks, allowing you to respond quickly and effectively.
Implement Alerts
Set up alerts for specific events, such as login attempts from unknown IP addresses or changes to SSH configurations, to stay informed of potential security issues.
Tools for SSH Security
Several tools are available to help enhance SSH security. Below are some popular options:
Fail2Ban
Fail2Ban is a tool that scans log files and bans IP addresses that exhibit suspicious behavior, such as multiple failed login attempts.
sshguard
sshguard is another log-based intrusion prevention tool that protects SSH servers from brute force attacks by blocking malicious IP addresses.
Keybase
Keybase simplifies the process of managing SSH keys, making it easier to securely share and manage keys across multiple devices.
Common SSH Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common SSH mistakes can help you maintain a secure remote access environment. Below are some mistakes to watch out for:
Using Weak Passwords
Weak passwords are easy targets for brute force attacks. Always use strong, complex passwords to protect your SSH connections.
Ignoring Software Updates
Failing to update SSH software can leave your system vulnerable to known vulnerabilities. Regular updates ensure that you have the latest security patches.
Overlooking Log Monitoring
Not monitoring SSH logs can result in missed opportunities to detect and respond to potential security threats. Regular log analysis is essential for maintaining SSH security.
Conclusion
Securing remote SSH access is a critical aspect of modern cybersecurity practices. By implementing the best practices, tools, and strategies outlined in this article, you can significantly enhance the security of your SSH connections and protect your systems and data from potential threats.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your current SSH configurations and implementing the recommended security measures. Additionally, please feel free to leave a comment or share this article with others who may benefit from it. Together, we can create a more secure digital environment.